This ancient star is racing through space at 600km/second
What's the story
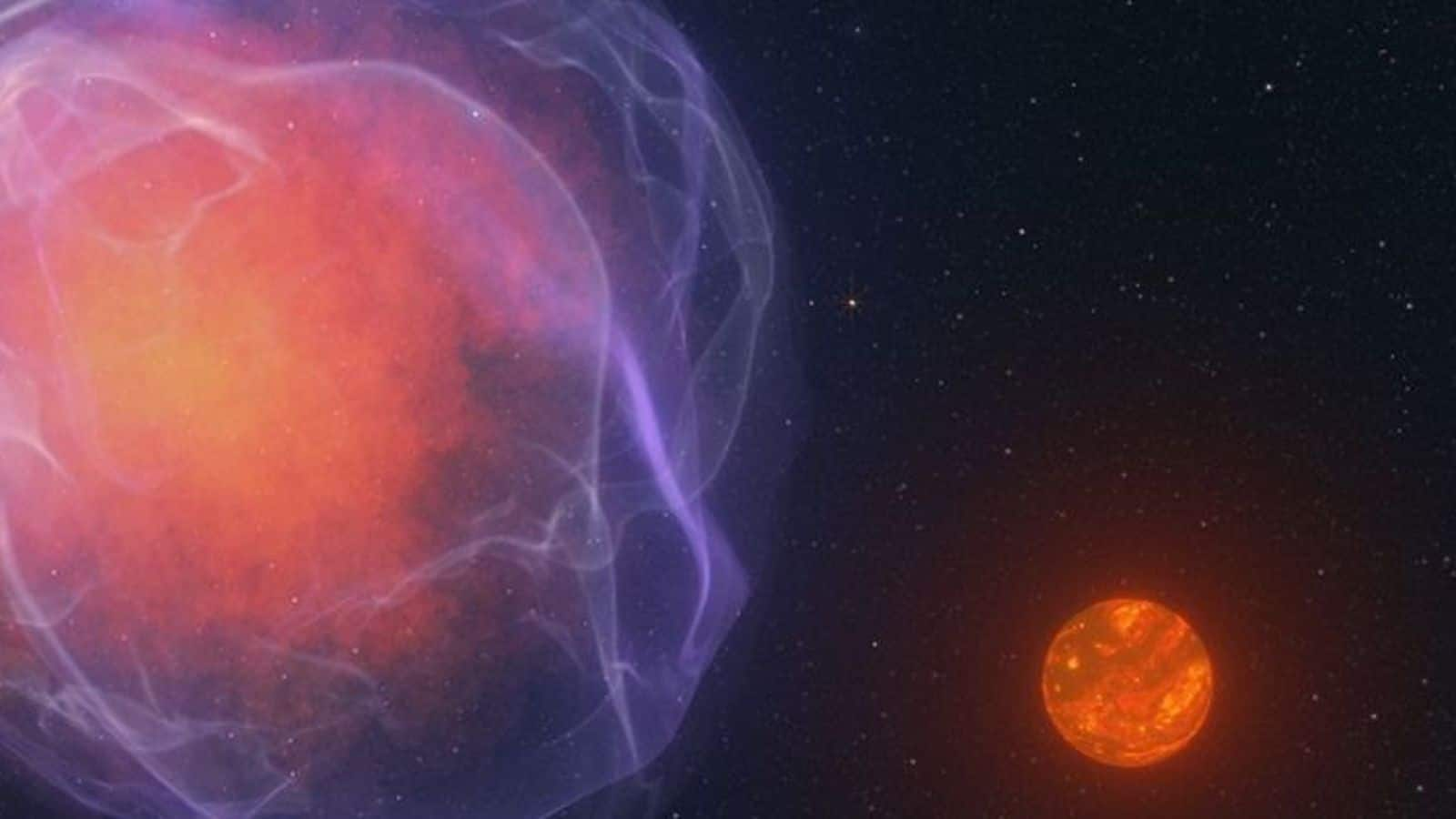
An ancient star, named CWISE J124909+362116.0 (J1249+36), has been observed moving through space, at an astonishing speed of nearly 600km/second. This velocity not only surpasses the galactic escape speed, but also makes it one of the fastest stars ever detected in the Milky Way. The star, identified by citizen scientists, is a rare type of small main sequence star called an L subdwarf, which makes it one of the oldest in our galaxy.
Hypotheses
Theories surrounding the star's high velocity
The star's extraordinary speed has led to several theories. Astrophysicist Adam Burgasser from the University of California, suggests that it could be the result of a supernova explosion, where the white dwarf is completely destroyed and its companion star is propelled at high speeds. However, he admits that this theory lacks definitive proof as there are no remnants left from the supposed supernova explosion.
Possibilities
Alternative theories and future research
Another theory, proposed by Caltech's astrophysicist Kyle Kremer, involves a star encountering a black hole binary within dense star clusters known as globular clusters. The third theory suggests that J1249 +36 might not be from the Milky Way at all, but rather from one of the several satellite dwarf galaxies orbiting it. To determine which theory is correct, scientists plan to examine the star's chemical composition in greater detail.