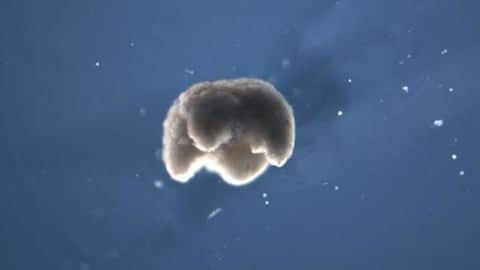
Meet Xenobots, first living robots that can self-heal
What's the story
In a major development, scientists have developed living robots that can heal on their own, like humans and animals. The machines, dubbed Xenobots, have been created from frog stem cells and are small enough to go inside human bodies one day and carry out tasks like delivering targeted medicines or disease-detecting sensors. Here's all you need to know about them.
Xenobots
Tiny bots can survive for weeks without food
Developed by scientists at the University of Vermont and Tufts University's Allen Discovery Center, Xenobots are tiny machines measuring less than a millimeter (0.04 inches) wide. They have been described as 'entirely new life-forms' that can not only heal on their own but also walk and swim, work in groups, and even survive for weeks without food. However, they can't reproduce or evolve.
Creation
How they created these bots?
To bring these robots to life, the scientists extracted living stem cells from the embryos of African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) and allowed them to incubate. Then, the incubated cells were cut and reshaped into different, never-seen-before body forms designed by a supercomputer. Guided by the design, and "aided by spontaneous self-organizing patterns", these robots moved on their own.
Information
Skills cells bonded bringing the machines to life
The researchers noted that the skin cells of Xenobots bonded automatically to form their structure while pulsing heart muscle cells allowed the machines to move, swim without any external stimuli.
Appearance
They look like blob of living flesh
It is worth noting that these living bots do not look like regular mechanically actuated metal/plastic machines. They are like biological machines that appear similar to a tiny blob of moving flesh. "These are novel living machines," said lead researcher Joshua Bongard. "They are neither a traditional robot nor a known species of animal. It's a new class of artifact: a living, programmable organism."
Self-healing
Plus, self-healing is an added advantage
Another notable fact about these bio-bots is that they can heal on their own; the researchers found this by slicing one robot and noting that it healed and kept moving. The team says that unlike traditional robots which "degrade over time and can produce harmful ecological and health side effects," the Xenobots are environment-friendly and safer for humans.
Potential uses
Many uses-cases possible with Xenobots
As Xenobots are biological, programmable, and capable of surviving in water without nutrients, the researchers think they can be used for a range of applications, especially targeted drug delivery inside humans. They could also be used to go inside our bodies to scrape out plaque or deliver tiny sensors capable of detecting internal diseases and problems.
Information
Even external uses are possible
Among other things, the Xenobots can be employed to clean up radioactive waste, collect microplastics in the ocean while helping humans gain more insight into cell biology and find ways to repair birth defects, critical injuries, even stop aging.