NASA's Curiosity rover documents Martian day and night
What's the story
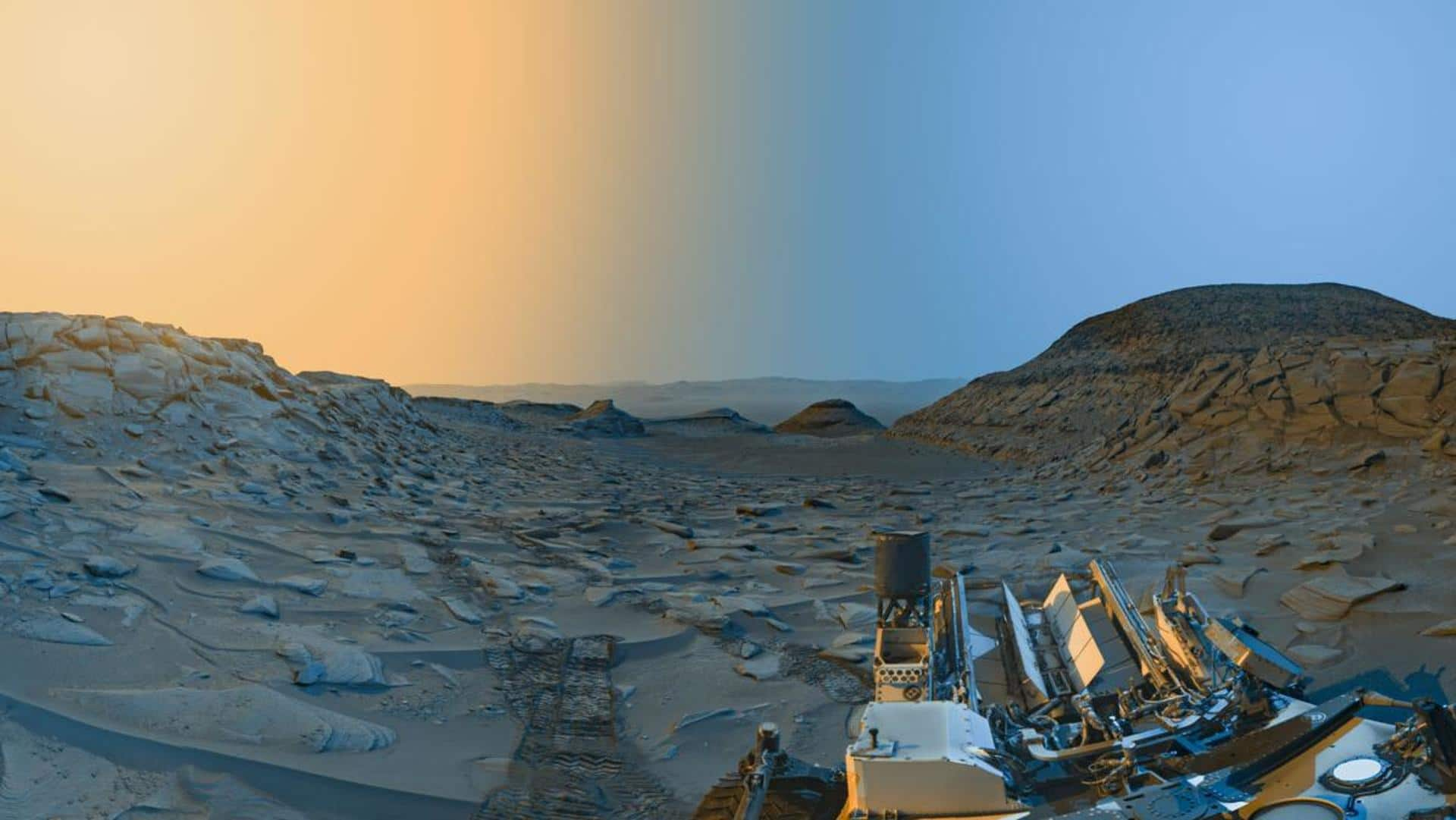
The latest image from NASA's Curiosity rover gives a visual representation of what morning and afternoon on Mars look like. Using its onboard navigation cameras, the rover captured two black-and-white panorama shots of Mars at different times of the day. NASA has also released a colored image by adding enhancements to the original black-and-white pictures to highlight the geological features of the Red Planet.
Context
Why does this story matter?
Curiosity is said to be the most capable rover ever sent to Mars. It reached the Red Planet in August 2012. The rover recently underwent a major software update, which allows it to drive faster. It has several onboard cameras, some of which help with navigation while others aid in scientific observations and allow us to better understand the Martian atmosphere.
Image
Blue and yellow represent morning and afternoon on Mars, respectively
The pictures were taken by the Curiosity rover on April 8 at 9:20 a.m. and 3:40 p.m. local Mars time. In the color-enhanced image, which was released on June 13, blue shades represent the panorama shot taken in the morning lighting, while yellow depicts the afternoon conditions on the planet. Curiosity previously captured a similar "postcard" picture in November 2021.
Image
It was winter on Mars when Curiosity captured the images
Curiosity took about 7.5 minutes to capture each of the panorama shots which were then send sent to Earth for processing. Also, it happened to be winter at the location where Curiosity captured these images. At that time, the dust was at its lowest in the Martian atmosphere, a factor that adds to the spectacularity of the images.
Region
The rover captured the image of Mount Sharp on Mars
In the image, the Curiosity rover is located at the bottom of a region called Mount Sharp on Mars. This terrain stands 5km tall within Gale Crater, where the rover has been probing since it landed in 2012. Further beyond lies Marker Band Valley, a winding area where the rover has discovered "unexpected signs of an ancient lake," said NASA in a blog post.
Details
The image also provides a glimpse of Curiosity itself
While the Martian landscape is the main highlight, the rear portion of Curiosity, including its antennas, is also seen in the image. The rover's Radiation Assessment Detector instrument, which appears as a white circle at the lower right corner of the image, has been helping scientists learn how to protect the first astronauts that will be sent to Mars from radiation on the planet.