These researchers created nanorobots to work inside human bodies
What's the story
Normally, it takes years to build a robot and make it smart enough to work in assembly lines or at airports.
But, in a major surprise, a group of researchers has developed a whole army of nanorobots in a matter of weeks.
They designed these machines with super-small legs and plan to use them for advancing the bounds of human anatomy.
Here's how.
Details
Laser-powered army of nanorobots
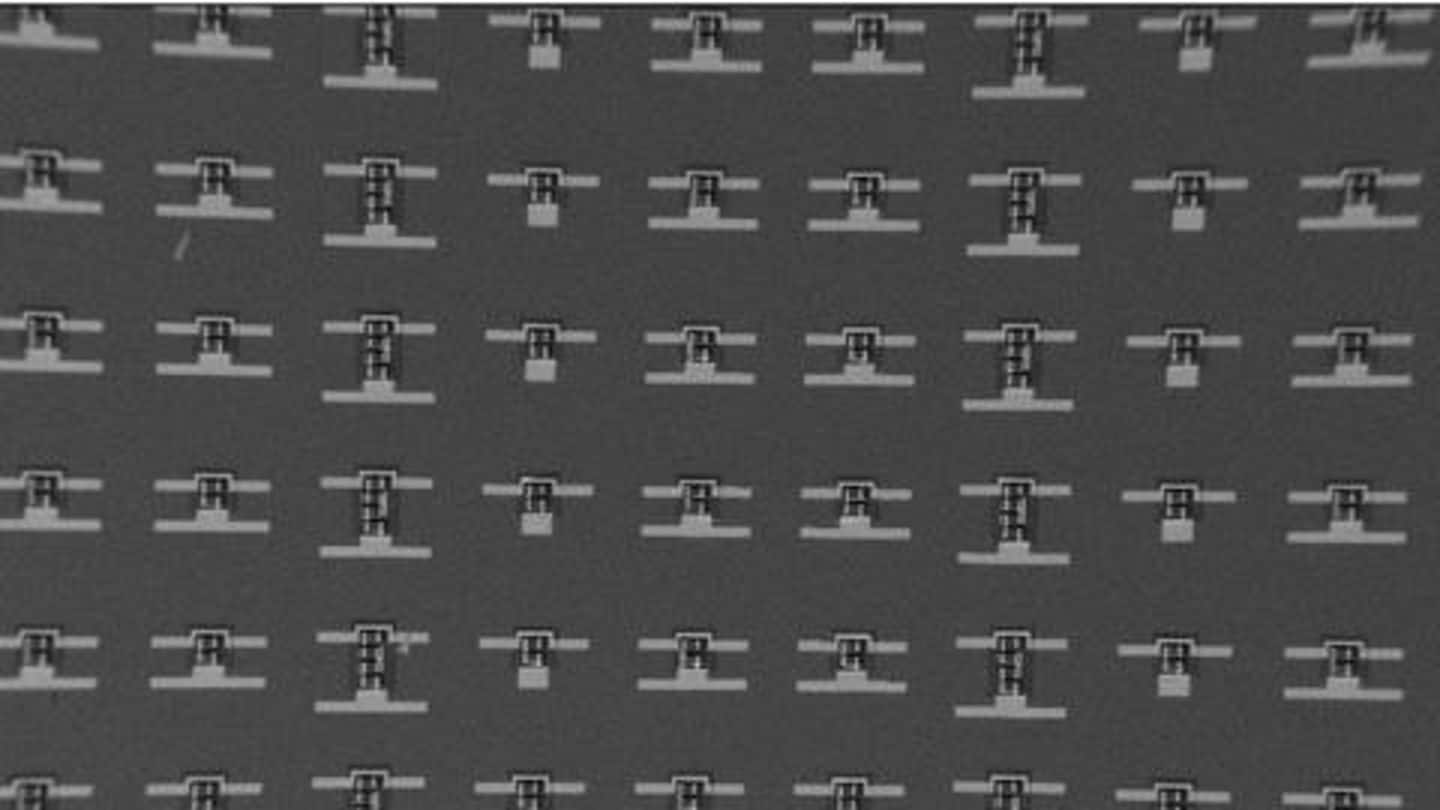
Using a 10cm-long silicon wafer and tiny solar cells, engineers from the University of Pennsylvania designed a million tiny little robots, Cosmos Magazine has reported.
The machines feature a glass body and can crawl around with their tiny 100 atoms thick legs, even in harsh environments.
Notably, the entire movement of the nanobots is generated through 'wireless power' transmitted into the bots' legs.
Quote
Also, despite being super small, the legs are very strong
"Each robot carries a body that's 1,000 times thicker and weighs roughly 8,000 times more than each leg," Marc Miskin, one of the researchers involved in the development of these bots, told Cosmos while highlighting the strength of the bots' tiny legs.
Working
But, how do they work?
The legs of the nanobots are made from a bilayer of platinum and titanium, while solar cells and other components are etched into a layer of silicon sitting on top of the body.
This way, when the engineers shine a laser on the solar panel, the platinum part expands but titanium stays rigid.
This results in contraction/relaxation of the legs, helping the machines walk.
Goal
These machines could open endless possibilities
Though imagining a million nano-sized bots in action doesn't paint a rosy picture, researchers hope to develop these machines for the benefit of humanity.
Specifically, they want to make these nanobots smart enough to work inside the human body.
Once that happens, they believe the robots will be able to perform a range of tasks, including things like delivering drugs or mapping the brain.
Issue
Still, it might be a while before that happens
These nanobots are already small enough to be injected into the human body but it might be a while before that actually happens.
This is because the walking range of the machines is not enough to meet the requirements for working inside the body.
To solve this, they are exploring other sources of energy such as magnetic fields to power the robots.