NASA's latest telescope will unlock the mysteries of black holes
What's the story
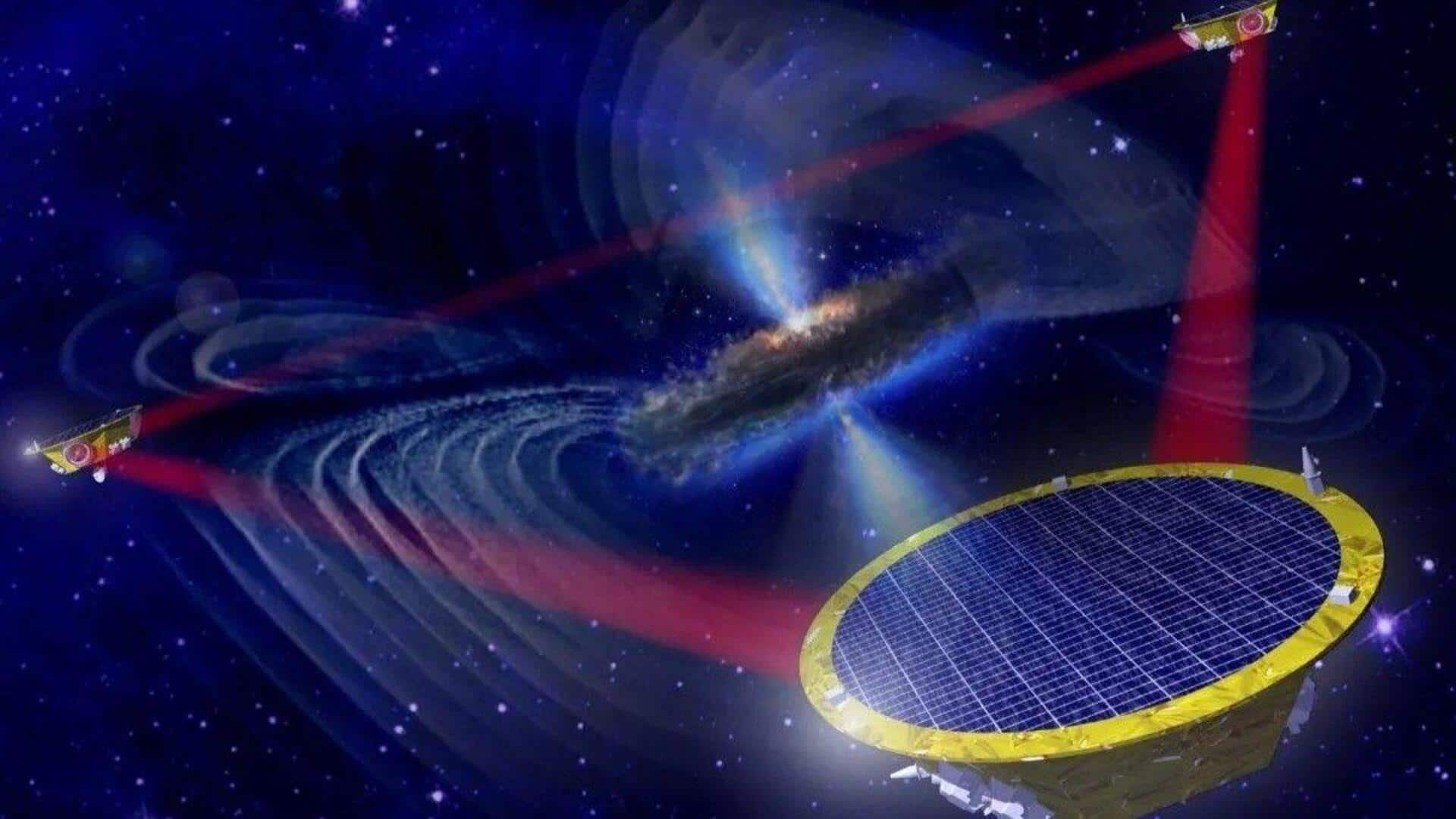
NASA has just unveiled a prototype of an innovative telescope, one that is designed specifically for a new space-based gravitational wave detection mission. The project is part of the Laser Interferometer Space Antena (LISA) mission, a collaborative effort led by the European Space Agency (ESA) with NASA's participation. The LISA mission aims to place three spacecraft in a triangular orbit nearly 2.57 million kilometers on each side.
Scientific discovery
Gravitational waves: A concept first proposed by Einstein
Gravitational waves, a concept proposed by Albert Einstein in 1916, are faint distortions in spacetime caused by massive cosmic events like colliding black holes. They carry information about the events that generate them, offering a unique window into the universe's most violent and energetic phenomena. Until now, scientists have relied on Earth-based detectors like LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) to capture gravitational waves. However, these instruments are limited by terrestrial noise and cannot detect waves from certain types of sources.
Mission details
LISA's revolutionary approach to detecting gravitational waves
LISA takes a different approach. This mission consists of three spacecraft arranged in a vast triangular formation, millions of kilometers apart. Infrared lasers will be used to measure the distance between these spacecraft with incredible precision. When a gravitational wave passes through the formation, it will cause minuscule changes in these distances, allowing LISA to detect the wave. The three spacecraft participating in the LISA mission will follow the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
Future prospects
LISA mission set for mid-2030s launch
The LISA mission is scheduled to launch in the mid-2030s. Detecting gravitational waves could provide "enormous potential" to improve our understanding of the universe, according to the official mission website. This includes studying events like black holes and the Big Bang that are difficult to study otherwise, further highlighting the importance of this groundbreaking project in the field of space exploration and research.