Chandrayaan-4: Know all about Chandrayaan-3's follow-up Moon mission
What's the story
Chandrayaan-3 stunned the world with its successful landing on the Moon and plans for its follow-up mission have already begun. Chandrayaan-4, which will also be called the Lunar Polar Exploration Mission (Lupex), will be a joint venture between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The ambitious mission seeks to investigate the presence of water on the Moon, which has been one of the most intriguing questions in lunar exploration.
Details
What will Chandrayaan-4's main objective be?
Chandrayaan-4's prime focus will be on the permanently shadowed regions (PSRs) on the Moon. The mission will aim to assess the quantity and quality of water in the PSRs at the lunar poles. The implications of finding water on the Moon would be huge. It would pave the way for sustainable human exploration. Previous observations have suggested the Moon could contain water. The upcoming mission would likely build on existing evidence and other knowledge we gain through Chandrayaan-3.
Mission
The mission will implement innovative technology
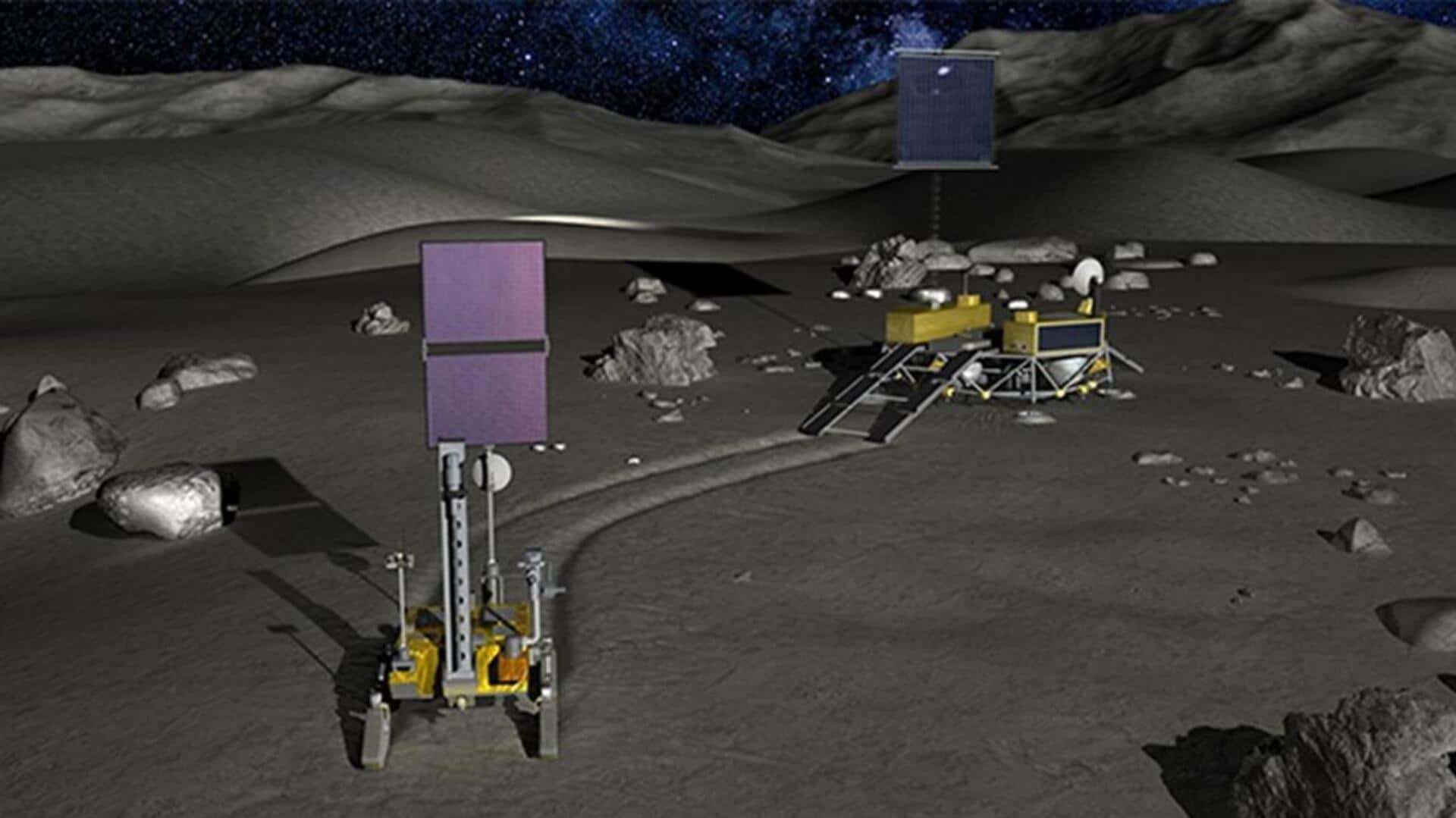
Chandrayaan-4 would comprise a lander and rover configuration. The mission will implement innovative technology to enhance the surface exploration of low-gravity cosmic bodies, per India Today. It is said to be equipped with thin-film solar cells and ultra-high-energy-density batteries to provide a sustainable power supply during the mission. These advancements also comprise improving the mobility solutions, bettering the survival mechanisms, and developing excavation techniques for potential mining operations.
Insights
Chandrayaan-4's anticipated launch timeline
Chandrayaan-4 is expected to launch in 2026. The mission will likely lift off aboard Japan's H3 rocket. This groundbreaking mission could provide valuable insights into the presence of water on the Moon and its potential uses for future crewed missions. This is of significance considering that there are ongoing plans, from NASA, to build a permanent moonbase. The mission will play a role in shaping the future of not just lunar exploration but also missions to Mars and beyond.