Chrome warns if your password has been leaked: Here's how
What's the story
In a bid to boost online security, Google has launched a tool that automatically checks if your password has been leaked anywhere on the internet. It comes in the form of a Chrome extension, named 'Password Checkup', and issues an alert if you are found to be using a breached password. Here's how you can use it to stay safe online.
Breach issue
Problem of data breaches: You just can't stop them
Data breaches are a common occurrence and, frankly speaking, there's no stopping them. You cannot stop hackers from breaking into sites, but the impact of their attacks can definitely be contained by having unique passwords for every service. This way, whenever a platform is compromised, you can just change the password for that account and everything else remains unaffected.
Need
However, you'll need to know which password has been compromised
In order to secure your account(s), you have to first know which username-password combinations have been compromised This is exactly where Google's Password Checkup comes in. Once you will install it and log in on a website, it automatically checks your details against a database of 4 billion leaked passwords to confirm whether the password you're using has been leaked or not.
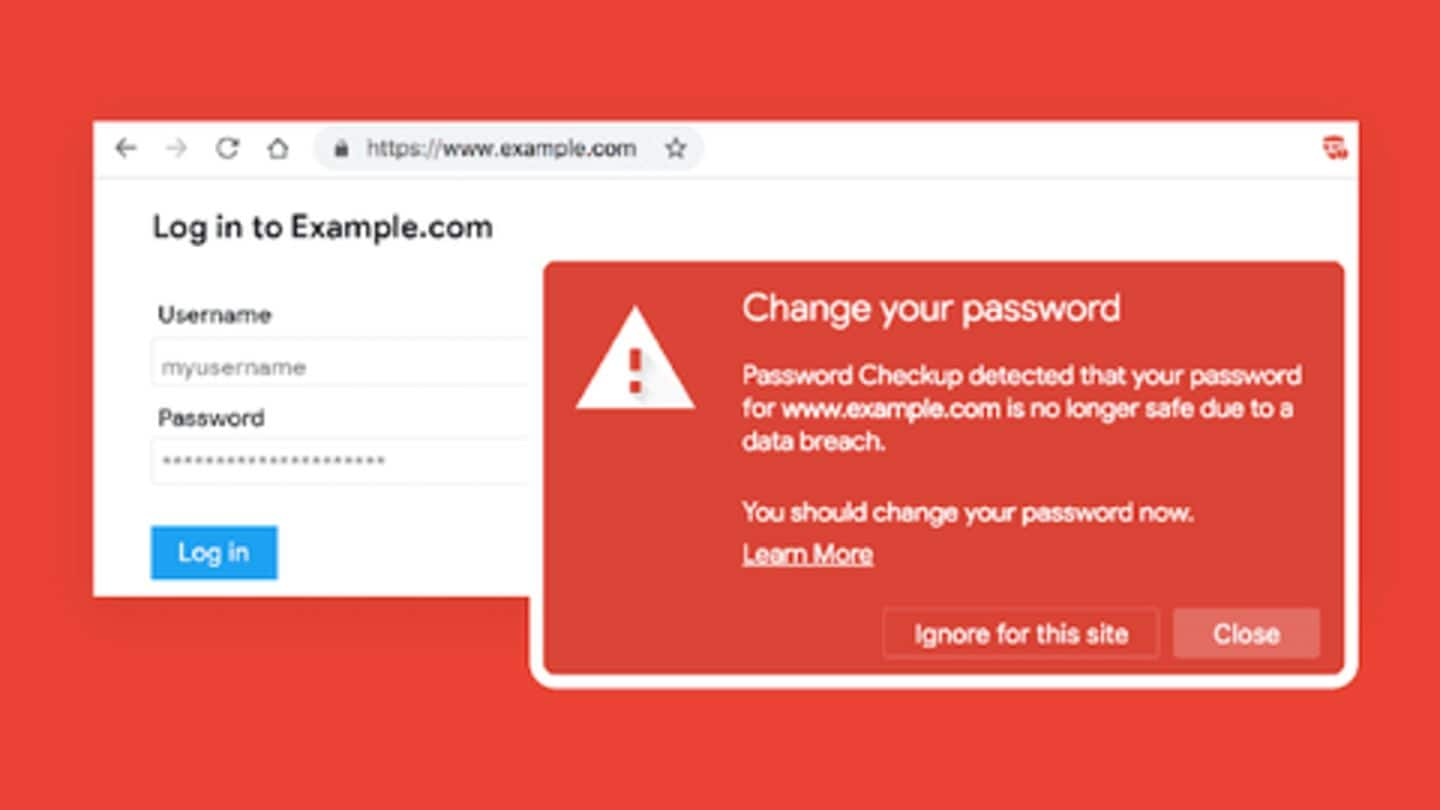
Warning
If a match is found, Google will alert you
If a match is found after scanning username-password, the extension will issue bold-red warning alert noting that the password you're using for logging in has been compromised. With this information, and the fact you're already logged in, you can change the password on the service in question and pick a new unique one. The password-picking process can be handled by any good password manager.
Security
Also, do note that every detail remains encrypted
As the process is dependent on sending data to Google, the search giant has emphasized it employs extensive techniques to keep your username and passwords safe. It keeps all leaked passwords and the ones they're matched against in a strongly hashed and encrypted form. Plus, the final matching happens locally, which is why nobody can ever know what your password is.