New AI tool can identify sex using dental X-rays
What's the story
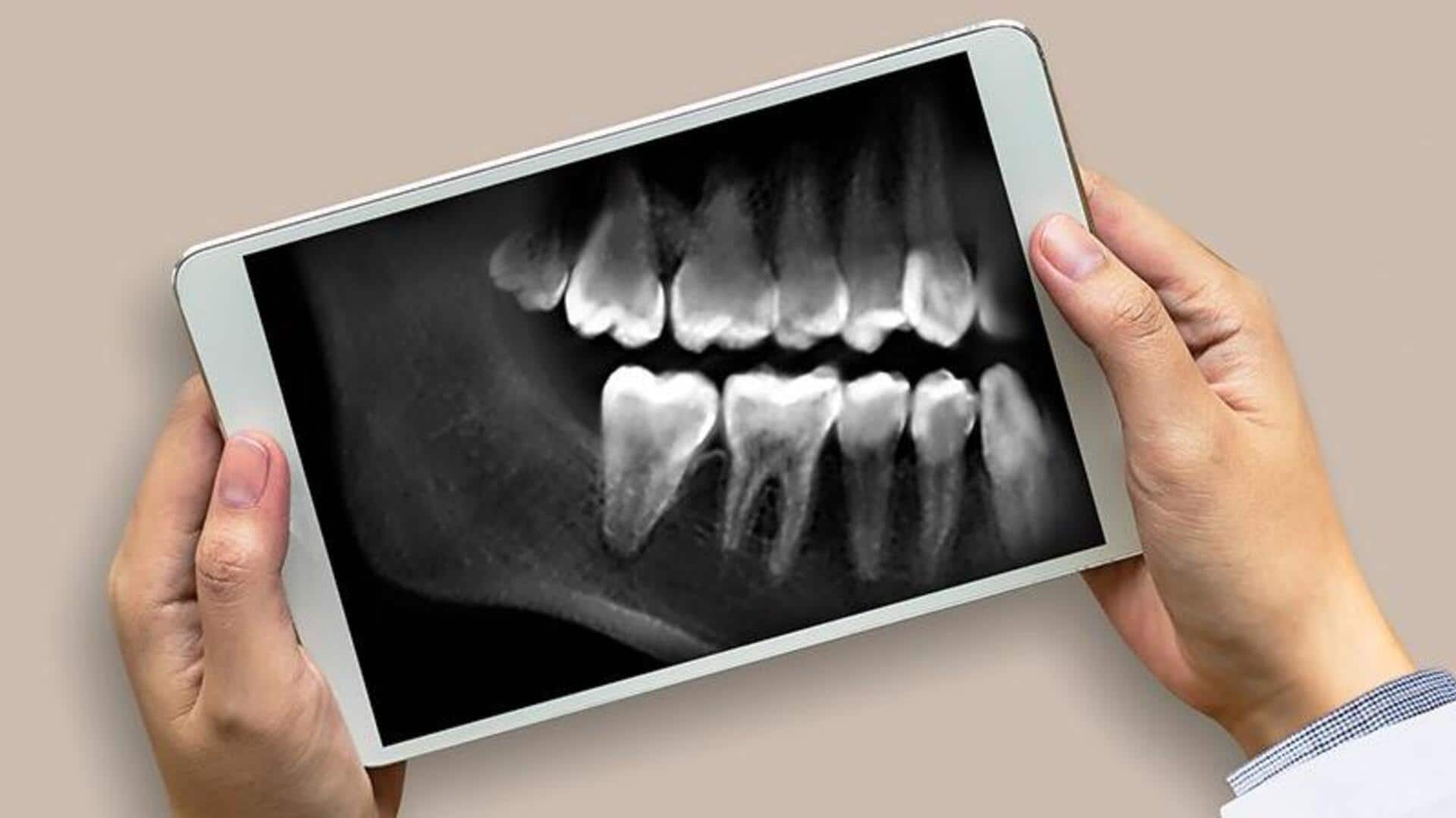
Brazilian researchers have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system that can accurately determine a person's sex using dental X-rays. The machine learning system, trained on over 200,000 panoramic radiographs, showed a remarkable 96% accuracy in estimating the sex of individuals aged over 16 years when high-resolution images were used. This AI-powered tool could assist forensic experts in identifying individuals from dental remains, mainly in challenging situations such as mass accidents or cases involving decomposed bodies.
Performance factors
Performance varies with age and image resolution
The study utilized two types of deep learning algorithms, a convolutional neural network and a residual network, both optimized to learn from dental X-ray images. The system's accuracy was found to be influenced by image resolution and age. Higher resolution images led to better performance, while the AI performed best for patients aged between 20 and 50 years (over 97% accuracy), slightly lower for those above 70 (just under 95%), and dropped significantly for individuals under the age of 16.
Future implications
Potential impact on traditional forensic methods
Traditional forensic methods often analyze bones and their structures to determine sex, but in some cases, only the jaw and teeth are available. The study shows that AI can extract key information from panoramic radiographs, which capture a comprehensive view of the mouth. By automating the sex determination process, AI could reduce human errors and enable faster identification, potentially revolutionizing forensic dentistry practices. It is important to note that this system was tested on images from living individuals.
Expanding horizons
AI's growing role in forensic dentistry and beyond
The successful application of AI in determining sex from dental X-rays opens up new possibilities for forensic dentistry. This breakthrough highlights the expanding role of AI across various fields. As research continues, further improvements and validations of such AI systems could lead to their broader adoption in forensic practices, ultimately enhacing the efficiency and accuracy of identification processes. However, the system's effectiveness may differ when applied to human remains in advanced stages of decomposition.