Busting myths about vitiligo
What's the story
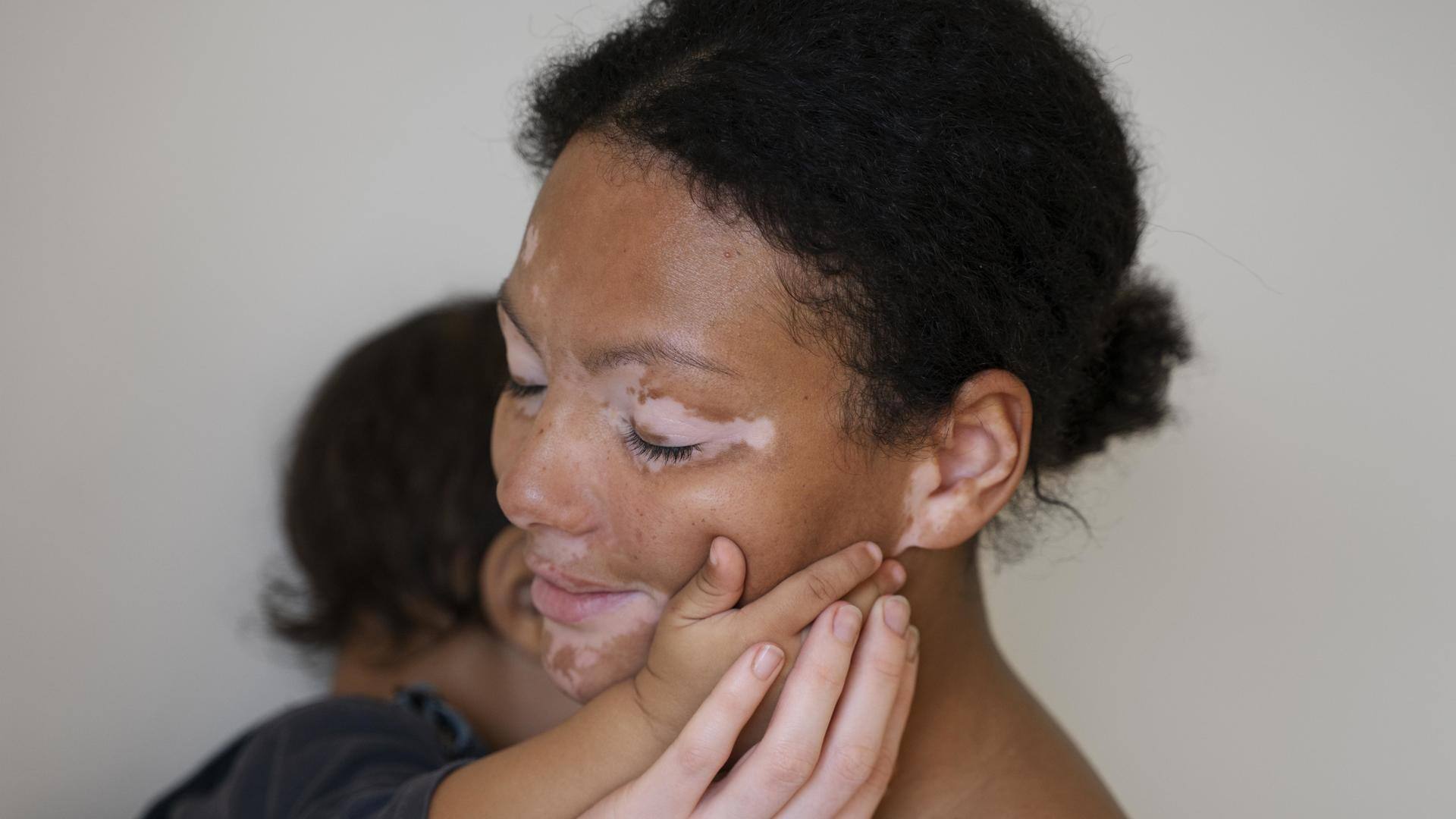
Vitiligo is a chronic, autoimmune health condition that causes white patches or pigmentation on the skin. It happens when melanocytes, which are responsible for the natural color of your skin, are destroyed by your own immune system. Today, let us debunk five of the most common myths surrounding this disease that make the lives of those suffering tougher.
Myth 1
Vitiligo is caused by diet
Many believe that vitiligo is caused by incorrect dietary practices, particularly when one consumes milk after eating fish. However, nothing of this is true, according to research. This condition is autoimmune in nature and has often been linked to factors including genetics and environment. Doctors have it that this ailment is entirely unaffected by food choices.
Myth 2
Vitiligo is contagious
What adds to the misery of those affected by vitiligo is that people avoid being around them as they fear getting infected. However, unlike many skin conditions, vitiligo is NOT contagious, which means that it does not spread from one person to another if they share the same things, eat together, touch each other, transfer blood, or indulge in sexual intercourse.
Myth 3
Vitiligo can be cured
Well, this myth is partially false. Although vitiligo treatments don't bring immediate results, they also don't help one regain their original skin color back. Treatment can only stop vitiligo from spreading to other body parts. Additionally, pigmentation may fade over time and patients have to consistently follow maintenance treatments to avoid that. The treatment can only stop or slow down discoloring.
Myth 4
Vitiligo is caused by sun damage
Many believe that vitiligo is caused due to overexposure to the sun. They also think that excessive use of bleach on the skin or overuse of skin whitening creams can lead to this condition. However, these beliefs are untrue as vitiligo is, again, an autoimmune disorder. It is more about the inner and deep layers of skin than the outer and exposed ones.
Myth 5
All white patches are vitiligo
Many skin-related issues can cause white patches and vitiligo is only one of them. These diseases include nevus, post-burns, leprosy, and some fungal infections, etc. Even the myth that vitiligo is related to leprosy or skin cancer is completely baseless, all three conditions are different from each other. In vitiligo, the production of natural skin pigment slows down or stops altogether.