What's sickle cell anemia that India would eliminate by 2047
What's the story
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, while presenting the Union Budget, announced plans to eradicate sickle cell anemia by the year 2047. Through this mission, the government aims to create awareness programs and conduct universal screening of seven crore people between 0-40 years of age. The government also aims to counsel those suffering from it. Read on to know about the disease in detail.
Sickle cell anemia
What is sickle cell anemia?
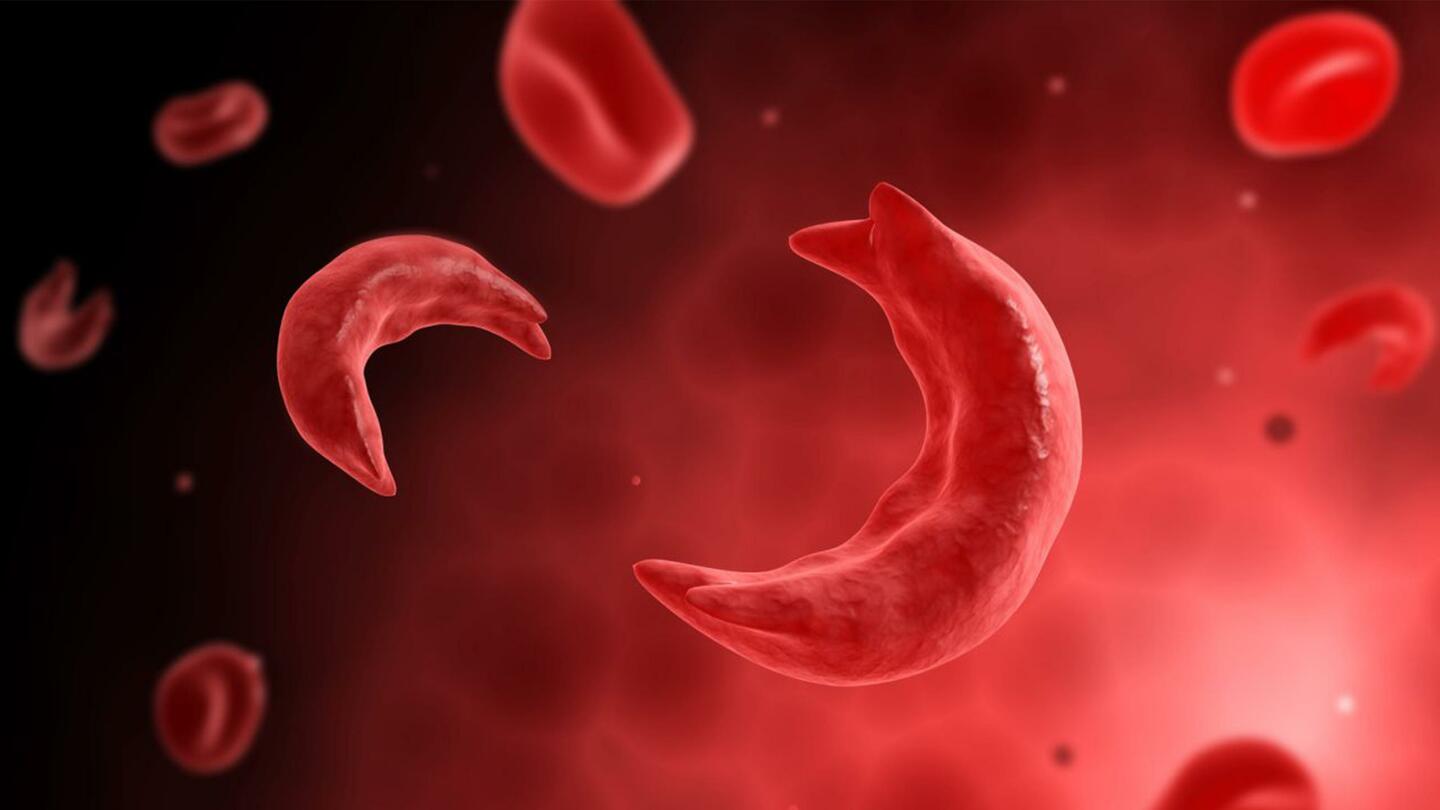
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic condition of red blood cells (RBCs). RBCs are usually shaped like disks, which allow them to travel seamlessly through even the smallest of blood vessels. But with this condition, the shape of the RBCs gets distorted, to almost resemble a sickle. This abnormal shape hinders or delays blood flow to the veins, causing pain and tissue damage.
Causes
What causes sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell anemia is caused by a mutation in the gene that is responsible for telling the body to make the iron-rich compound in red blood cells called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin facilitates red blood cells to carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. The hemoglobin associated with sickle cell anemia causes red blood cells to become rigid, sticky, and deformed.
Who's more prone
Who is at risk for sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood condition that is particularly common in people with an African, Indian, or Caribbean family background. Mostly children under the age of three are prone to the risk of getting sickle cell anemia. In India, this genetic condition is widespread among the tribal population. It affects about 1 in 86 births among the Scheduled Tribes.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms?
Though there are multiple types of sickle cell anemia, they all show similar symptoms. These symptoms may include excessive fatigue or irritability, fussiness, bed-wetting from associated kidney problems, jaundice, swelling and pain in hands and feet, and pain in the chest, back, arms, or legs. These symptoms usually appear in babies as early as four months old, but generally occur around the 6-month mark.
Treatment
What does the treatment involve?
There are several treatments available that can help you overcome the symptoms of the disease. Your doctor may recommend intravenous fluid rehydration, as it can help in the normalization of red blood cell function. Your doctor may also treat infections to control the disease. Painkillers, supplements to improve oxygen levels in the blood, and bone marrow transplants are some other treatment options.