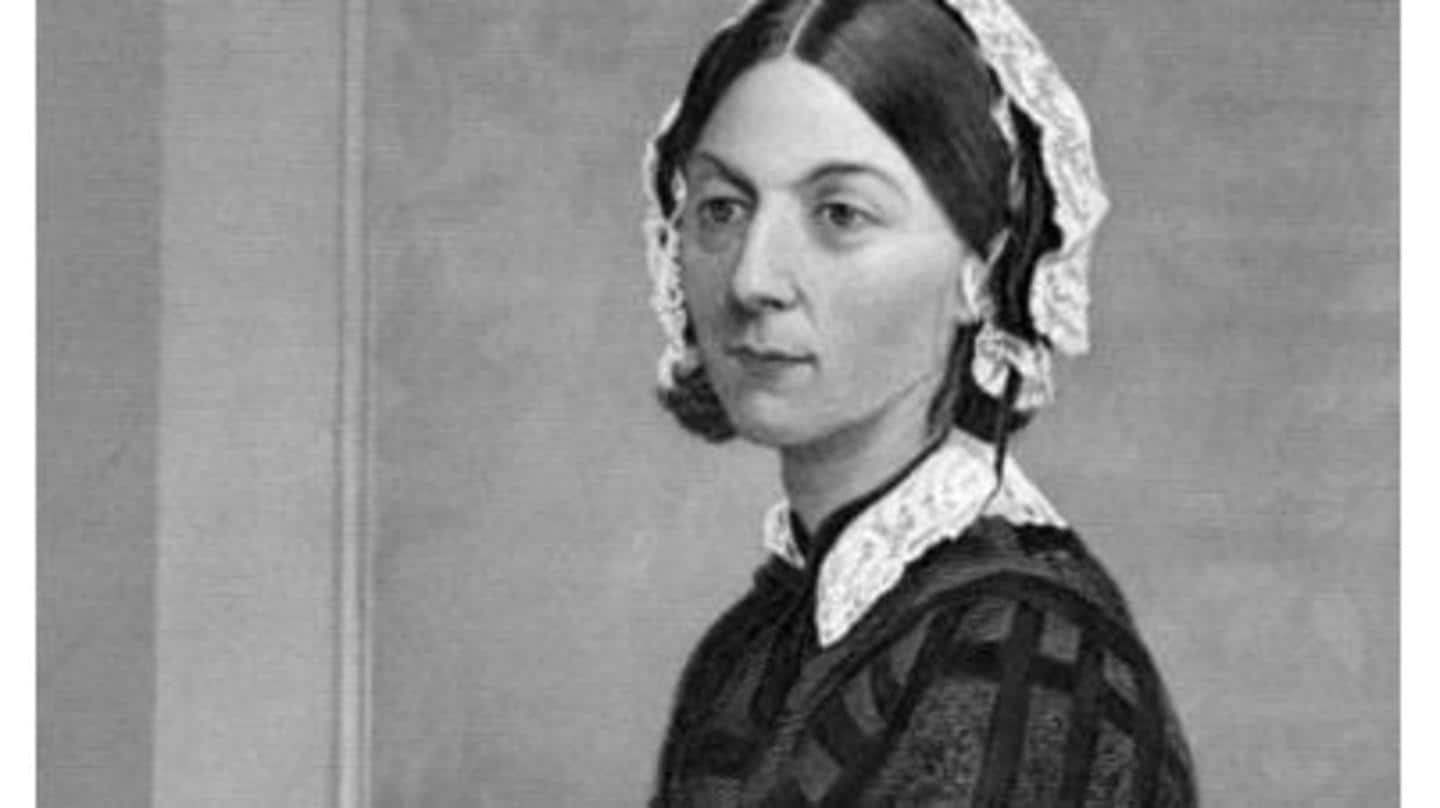
International Nurses Day 2022: The legend that was Florence Nightingale
What's the story
International Nurses Day is observed every year on May 12 to celebrate the birth anniversary of Florence Nightingale, the founder of modern nursing.
The day was established by the International Council of Nurses (ICN) in 1965 and was originally planned by Dorothy Sutherland of the U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare.
Read on to know more about Nightingale's contribution to the health sector.
Career beginnings
Nightingale pursued nursing despite her parents' objections
Nightingale was born on May 12, 1820, into a wealthy British family.
During that time, nursing was considered a job of low social status, and nurses also went through alcohol abuse.
At the age of 16, Nightingale chose to pursue nursing despite her parents' objections. In 1850, she started medical training.
Nightingale was posted as the Superintendent of a women's hospital in 1853.
Lady with the Lamp
How she became 'Lady with the Lamp'
During the Crimean War that was fought between 1853 and 1856, Nightingale along with 38 women volunteer nurses arrived at the Barrack Hospital in Scutari and witnessed several injured soldiers.
Many had contracted several infections as well.
Nightingale started treating the wounded British troops and attended to them round-the-clock with a lamp in hand.
This earned her the title of "Lady with the Lamp."
Pie chart
She popularized the pie chart
Nightingale was also known as a great statistician.
She is credited with popularizing the pie chart, even though it was first drawn in 1801 by William Playfair.
The pie chart used by her was called "coxcomb" which she designed along with British epidemiologist William Farr.
The pie chart illustrated the number of unwarranted deaths caused due to preventable infections during the Crimean War.
Achievements
About her achievements
Throughout her career, Nightingale excelled in sanitary health.
She worked toward establishing nursing as a respected profession and in 1859, she published her first book Notes on Nursing: What it is and What it is Not.
In 1860, Nightingale established the first scientifically-based Nightingale School of Nursing in London.
In 1907, she became the first woman to receive the order of merit.
Legacy
Legacy continues even after her death
Nightingale passed away at the age of 90 on August 13, 1910.
Following her death, the International Committee of Red Cross initiated the Florence Nightingale Medal which is awarded to nurses every two years for their extraordinary service.
On International Nurses Day, the Indian President honors nurses with the National Florence Nightingale Award annually.
There are three statues dedicated to Nightingale in Derby, England.