India to have most overweight youth by 2050: Report
What's the story
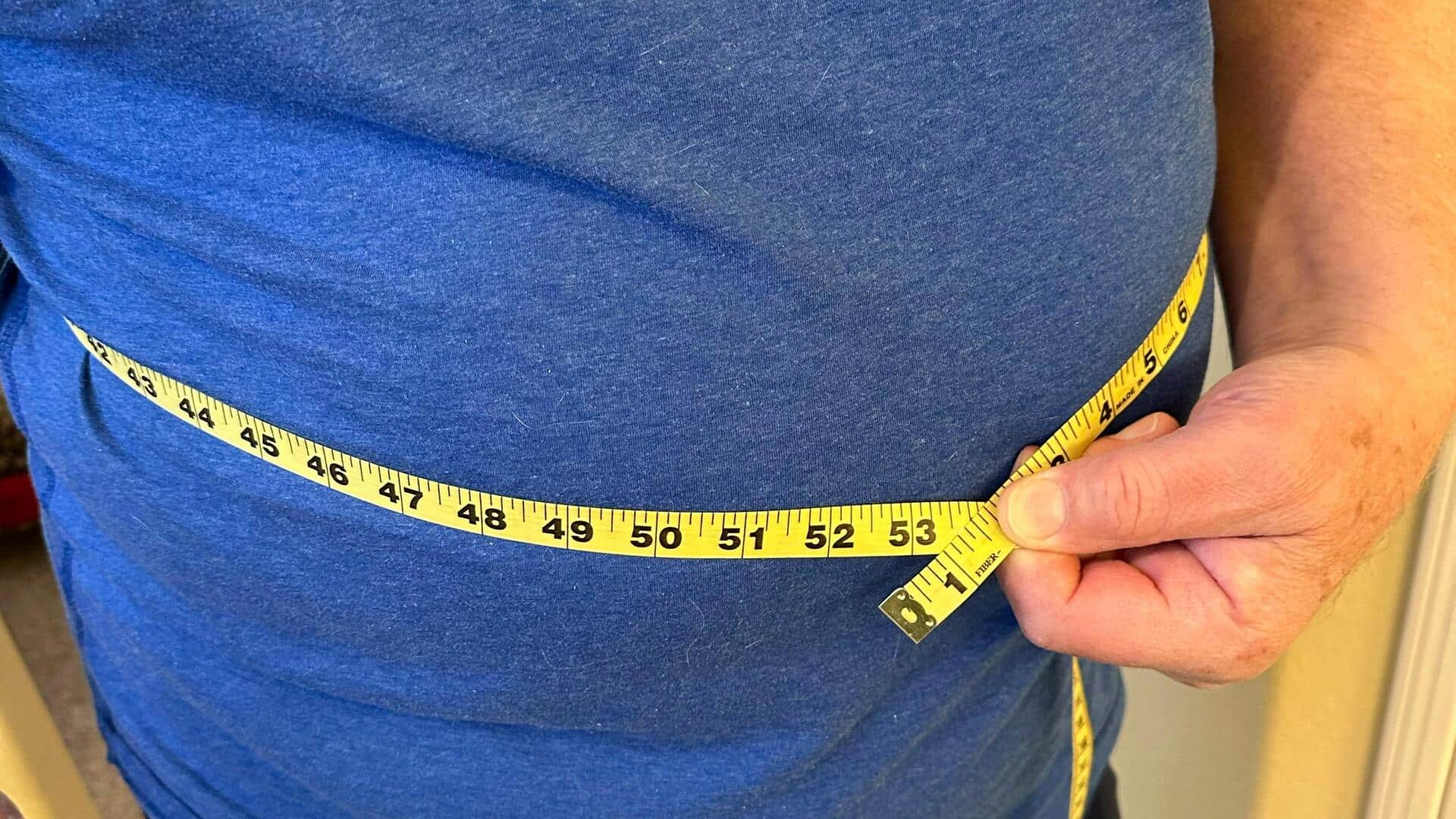
India will have the most overweight or obese young people aged 15-24 by 2050, a new analysis published in The Lancet has revealed.
In the 5-14 years age group, India will come second after China.
By mid-century, the country will house an estimated 450 million overweight or obese adults, nearly 12% of the global population in this category.
Health initiative
PM Modi launches anti-obesity campaign
In light of these shocking projections, Prime Minister Narendra Modi has launched an anti-obesity campaign to encourage fitness and healthy lifestyles across India.
Addressing the National Games recently, he spoke about the risks of obesity-related non-communicable diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
The PM stressed on the need for exercise and a balanced diet, especially cutting down on unhealthy fat and oil in food.
Rising numbers
Global obesity trends and India's contribution
The Lancet study predicts that if current trends continue, half of all adults and a third of children across the globe will be overweight or obese by 2050.
The Global Burden of Disease Study BMI Collaborators attribute this to major global failures causing obesity rates to rise over the last three decades.
In 2021 alone, India had 179.6 million overweight/obese adults, a number set to skyrocket by 2050.
Lifestyle impact
Unhealthy lifestyles and processed foods fuel obesity
The study measured obesity using body mass index (BMI) for adults and International Obesity Task Force criteria for those under 18.
It discovered that recent generations are gaining weight faster and at younger ages, raising risks for diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular issues.
Dr. Ambrish Mithal from Max Healthcare emphasized that easy access to ultra-processed foods and sedentary lifestyles greatly contribute to rising obesity rates in India.
Global distribution
Overweight adults concentrated in 8 countries
The study also found that more than half of overweight or obese adults worldwide live in eight countries: China, India, the United States, Brazil, Russia, Mexico, Indonesia, and Egypt.
To combat this crisis, the governments are urged to implement strategies that improve nutrition and physical activity while transforming diets within sustainable food systems.
The Lancet study warns that without immediate action, the economic impact due to increased healthcare costs could be "staggering."