Different levels of self-driving technology in cars, explained
What's the story
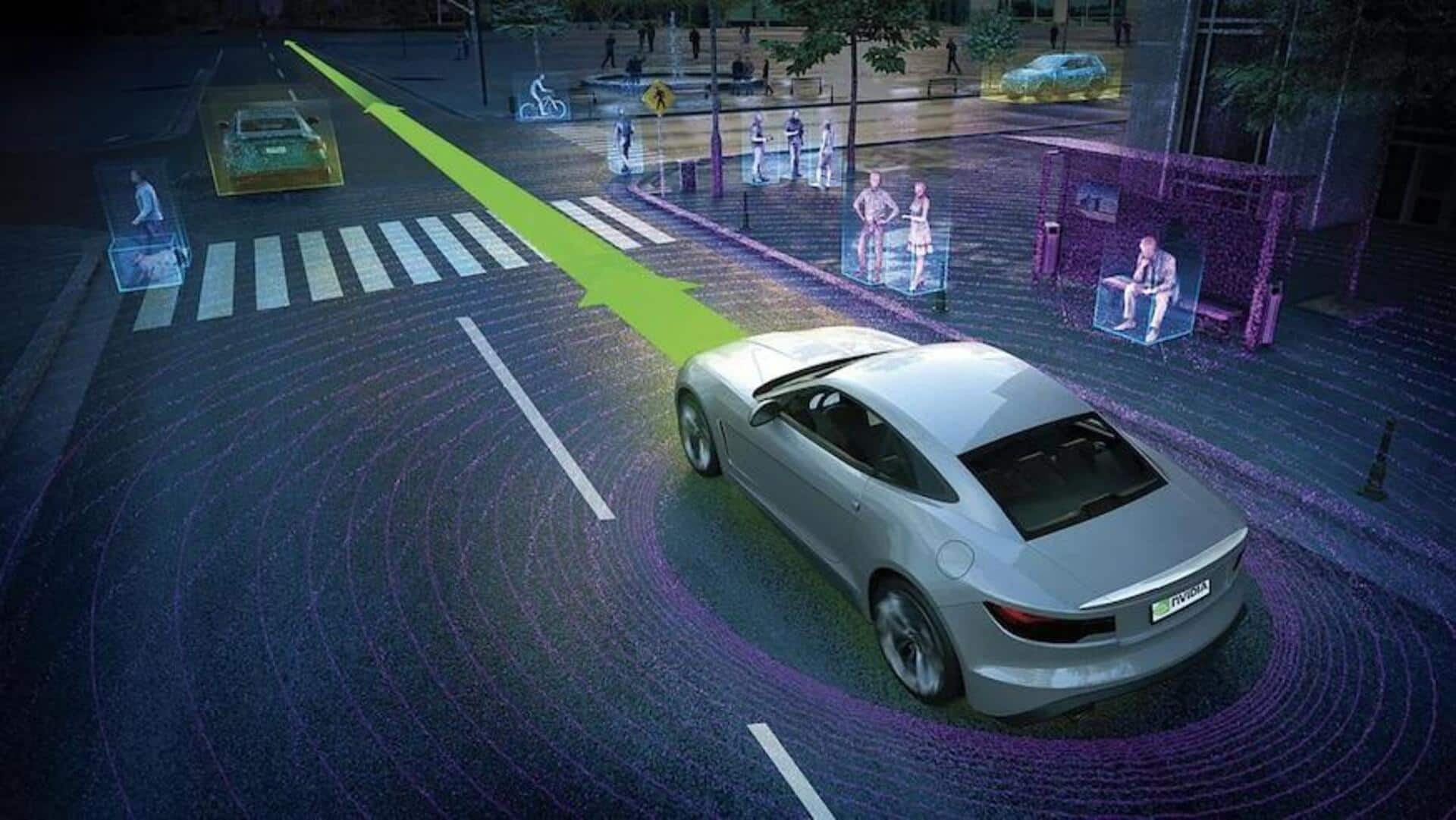
With AI becoming an integral part of the automotive industry, self-driving cars are becoming more intelligent than ever before. Although the technology is still years away from becoming available in mass-produced vehicles, many automakers are testing higher levels of automated driving on their latest cars. But how are different levels of self-driving cars classified? What does each level mean? Let's find out.
Context
Why does this story matter?
Autonomous or self-driving cars have been widely showcased in sci-fi movies such as I, Robot, or Minority Report. However, with advancements in radar/LiDAR as well as the integration of AI in the control units of modern cars, automakers such as Tesla are pushing the boundaries of self-driving technology. Autonomous driving technology is classified into six levels by SAE International.
Level #1
Level 0: No Automation
At Level 0, the automated system issues warnings and can momentarily intervene if needed, but has no sustained control over the vehicle. This is found in modern cars with camera-based automated braking systems. While the system has the ability to pre-charge and apply brakes when needed, it demands human intervention via beep sound or visual warnings to complete the action.
Level #2
Level 1: Driver Assistance
Level 1 is commonly referred to as Advance Driver Assistance System (ADAS). At this level, both the driver and automated system share control of the vehicle's steering and braking mechanics. The system utilizes a combination of radar, ultrasonic sensors, and cameras to provide functions such as adaptive cruise control and automated parking assistance. This system is gaining popularity with cars globally.
Level #3
Level 2: Partial Automation
Level 2 or ADAS Level 2 has the ability to take full control of the vehicle's acceleration, braking, and steering needs, with periodic human intervention. Generally seen on high-end cars, this system uses cameras and other relevant sensors to make sure that the driver is paying attention on the road, even when their inputs are not needed. Actual hands-off driving is considered Level 2.5.
Level #4
Level 3: Conditional Automation
From Level 3 onward, the automated system can take full control of the driving part for most situations. However, even at this level, the system will prompt human intervention in situations such as diversions/blockages on the road or in extreme weather such as rain/snowfall, which can hinder the camera and/or sensor's input. Tesla is currently testing a beta version of Level 3 self-driving.
Level #5
Level 4: High Automation
As with Level 3, minimum driver attention is required at Level 4. At this level, the system will keep functioning, even when the driver is asleep or not in the driving seat. Such a type of self-driving ability is supported in limited areas (geofencing). An example of Level 4 autonomy is the robotic taxi service (Cruise) currently operational in San Francisco, California since 2022.
Level #6
Level 5: Full Automation
As the name suggests, Level 5 or Full Autonomous driving does not require human intervention at all. Although such systems are currently in the early development stage, automakers are positive of making rapid progress with the evolution of AI algorithms and electronic control units of the vehicles. At this level, the system is intended to work in any weather or surface condition.